How Does AI Play Role on Sustainable Entrepreneurship In The Digital Age?

Rajibul Islam, MBA in Digital Business and Management
Eva Holmberg (Lic.Sc. Econ.), Educator for Master degree programmes at Novia University of Applied Sciences
As the future of our planet is threatened by climate change and loss of biodiversity sustainable development has become a priority for both governments and businesses worldwide. For businesses, Artificial Intelligence (AI) can play a pivotal role in enhancing green business strategies as AI makes it possible to optimize resource utilization, reduce waste, and thereby mitigate environmental impacts. For many companies AI offers a possibility to operate in a sustainable way which often result in a competitive advantage and significant business benefits with a high return on investment. The intersection of AI and sustainable development is crucial for promoting green business practices and achieving Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). This topic is in the MBA thesis of Rajibul Islam (2024) explored through a comprehensive literature analysis and 25 episodes of TEDx Talks, revealing AI's transformative potential in sustainable entrepreneurship (Islam, 2024).
According to experts providing the TEDx Talks, AI significantly enhances green business practices by offering innovative solutions to environmental challenges and improving sustainability across various industries. It revolutionizes business operations through efficient resource management, waste reduction, and environmental impact mitigation. Key areas where AI promotes green business practices include optimizing processes, fostering innovation, optimizing supply chains, enabling real-time monitoring, and managing environmental impacts (see Figure 1).
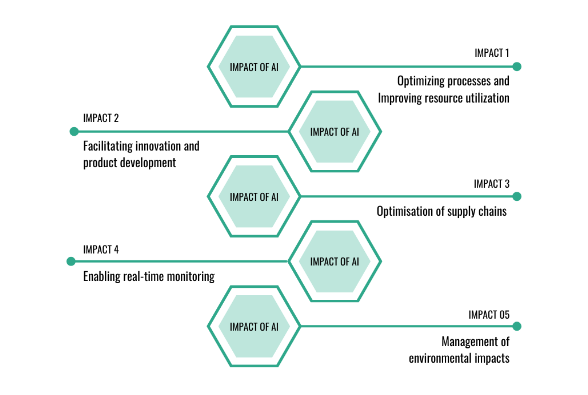
Figure 1. Impact of AI on promoting and implementing green business practices
AI's impact on optimizing processes and improving resource utilization is profound. AI-powered systems analyze large datasets to identify efficiency opportunities. For instance, in agriculture, AI enhances irrigation by examining soil quality and weather trends, reducing pesticide use, and increasing crop yields. This predictive capability allows businesses to make data-driven decisions, decreasing resource use and environmental impact. AI also drives innovation by helping companies to develop sustainable products like biodegradable materials and energy-efficient technologies, meeting consumer demand for eco-friendly options and boosting market differentiation.
AI also enables real-time monitoring and management of environmental impacts through AI-powered sensors and monitoring systems. These systems track energy usage, emissions, and waste generation, allowing businesses to promptly identify inefficiencies and implement corrective actions. AI-based predictive maintenance optimizes equipment performance, reducing downtime and minimizing environmental risks. Furthermore, AI-driven supply chain management systems enhance transparency and accountability in sourcing and production processes, helping businesses reduce carbon emissions, waste, and promote fair labor practices. Overall, AI provides businesses with transformative opportunities to foster sustainability, enhance competitiveness, and transition towards a more sustainable economy.
Businesses face challenges in using AI for sustainability, primarily due to the high cost, complexity, and specialized expertise required, which can be prohibitive for small enterprises. Ethical concerns like data privacy, algorithmic bias, and unintended consequences also need careful management. Overcoming these barriers involves responsible and transparent AI deployment, strong data governance, and stakeholder engagement.
Despite these challenges, AI offers significant opportunities to enhance sustainability by optimizing resource use, reducing waste, and mitigating environmental impacts. AI can also drive the creation of innovative sustainable products and services. By fostering collaboration and knowledge sharing through AI platforms, businesses can accelerate innovation and drive systemic change towards a sustainable future, contributing to a resilient and prosperous society.
For Further Reading
- Bickley, S. J., Macintyre, A., & Torgler, B. (2021). Artificial Intelligence and big data in sustainable entrepreneurship. CREMA Working Paper, No. 2021-11. Center for Research in Economics, Management, and the Arts (CREMA), Zürich. http://hdl.handle.net/10419/234626
- Fuerst, S., Sanchez-Dominguez, O., & Rodriguez-Montes, M. A. (2023). The Role of Digital Technology within the Business Model of Sustainable Entrepreneurship. Sustainability, 15(14), 10923. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151410923
- Islam, R. (2024). Sustainable Entrepreneurship in the Digital Age: The Role of AI in Green Business Practices. MBA thesis, Novia University of Applied Sciences. https://urn.fi/URN:NBN:fi:amk-2024060521089
- McCarthy, J. (2007). What Is Artificial Intelligence? Stanford University. http://jmc.stanford.edu/articles/whatisai/whatisai.pdf
Sort Bibliography about Authors
 Rajibul is the main writer and has worked as a manager in the gas and oil sector for seven years in Bangladesh. In addition, he is also a graduate from USTB in China and wants to adopt Finnish culture now. In his spare time, Rajibul enjoys painting, designing, writing, watching movies, travelling and photography.
Rajibul is the main writer and has worked as a manager in the gas and oil sector for seven years in Bangladesh. In addition, he is also a graduate from USTB in China and wants to adopt Finnish culture now. In his spare time, Rajibul enjoys painting, designing, writing, watching movies, travelling and photography.
 Ms. Eva Holmberg (Lic.Sc. Econ.). Eva Holmberg works as educator for Master degree programmes at Novia University of Applied Sciences. Eva Holmberg has a long experience in teaching sustainable tourism and research methods in higher education, research, and international project management.
Ms. Eva Holmberg (Lic.Sc. Econ.). Eva Holmberg works as educator for Master degree programmes at Novia University of Applied Sciences. Eva Holmberg has a long experience in teaching sustainable tourism and research methods in higher education, research, and international project management.
The blogpost has been reviewed by Novia's editorial board and accepted for publication on 13.6.2024.
![]()
MBA Insights
The Novia MBA Insights blog features peer-reviewed posts authored by MBA graduates and their supervisors. Its aim is to disseminate pertinent insights and findings from MBA thesis research.
The subject matter encompasses business, leadership, digitalisation, design thinking, services, project development, and may also touch on societal issues. Posts are selected for their relevance to professionals in the field or the general public.
All blog entries undergo review by a faculty editor and subject matter experts.
We follow CC-BY if nothing else is stated.
Disclaimer: The author(s) are responsible for the facts, any possible omissions, and the accuracy of the content in the blog.The texts have undergone a review, however, the opinions expressed are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the views of Novia University of Applied Sciences.
Posta din kommentar
Kommentarer
Inga har kommenterat på denna sida ännu