Adopting AI-Driven Solutions in Renewable Energy: A Case Study in Ostrobothnia, Finland

A Case Study in Ostrobothnia, Finland
The renewable energy sector is rapidly evolving, driven by increasing technological advancement and global sustainability demands. In order to stay competitive, increase innovative service offerings, and improve day-to-day efficiency the integration of advanced technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI) and robust database management systems is becoming critical. AI has emerged as a game-changer in the energy sector, with applications ranging from optimizing renewable energy sources (like wind and solar) to predicting energy demand and maintenance. By processing vast datasets, AI can optimize energy grid integration, forecast energy production, and significantly improve operational efficiency.
In the following discussion we will present an extract from Ali’s master thesis research in the renewable energy sector. We will firstly introduce a new integrated conceptual framework which is used in the study, secondly, we will explore a case study from a Finnish renewable energy consultancy that demonstrates challenges to AI adoption, a strategic road map on AI implementation and finally our thoughts on AI as a necessity for future competitiveness.
The conceptual framework: Integrating AI and database technologies
Successful AI adoption requires more than just implementing new technologies; it demands a holistic approach that aligns with a company’s technological setup, workforce readiness, and strategic objectives. This case study in a Finnish renewable energy consultancy introduces an integrated conceptual framework, developed by combining three well-established models to provide a structured roadmap for AI integration:
- Technology Acceptance Model (TAM): This model evaluates employee acceptance by focusing on how useful and easy-to-use they perceive AI tools to be.
- Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT): Adding elements like social influence and expected performance, this theory addresses organizational and social dynamics affecting AI adoption.
- Cross-Industry Standard Process for Data Mining (CRISP-DM): CRISP-DM guides data management, covering business understanding, data preparation, modelling, and evaluation—essential steps for handling large data volumes effectively.
This framework ensures AI integration addresses both human and technical factors, along with leadership, strategic goals, competitor approaches, and social influence. It supports operational efficiency and aligns AI use with company objectives. The study used advanced statistical methods to evaluate AI readiness, focusing on relationships between critical factors like perceived usefulness and behavioral intentions, providing actionable insights and highlighting areas for improvement.
By examining these relationships, the study identified how ease of use influences employees’ intent to adopt AI tools, while organizational factors play a moderating role. These insights offer a valuable roadmap for enhancing readiness and optimizing the integration process, ensuring that AI adoption aligns with both workforce and organizational goals.
Challenges to AI Adoption
Despite the potential of AI, many companies encounter significant obstacles when attempting to implement it. The case study identified two major challenges:
- Technological gaps: While the company already had advanced digital tools, which recently have AI-powered functionality, it faced difficulties in integrating these tools across platforms, which led to inefficiencies and data fragmentation.
- Cultural resistance: AI adoption often requires a cultural shift. In the case study, employees expressed concerns about job displacement and their ability to adapt to AI too.
To overcome this, leadership is needed to foster an environment of trust, innovation, and continuous learning, by promoting open communication, addressing employee concerns, aligning AI initiatives with strategic goals, and supporting upskilling programs—empowering employees to embrace AI confidently and collaborate effectively in a culture of adaptability and growth.
A strategic roadmap for AI implementation
The integration of AI is crucial for managing complex renewable energy data, forecasting trends, and optimizing project workflows. AI enables data-driven decisions, streamlining processes such as predictive maintenance, resource allocation, and client engagement, which are essential for scaling up the company’s renewable energy projects.
To ensure the smooth adoption of AI, the study recommends a phased approach to AI adoption, starting with small pilot projects and expanding gradually. The roadmap, known as the “On the Move” 2-10-3 Strategy, includes:
- 2x2 matrix: This approach helps to prioritize AI use cases based on their values and potential business impact.
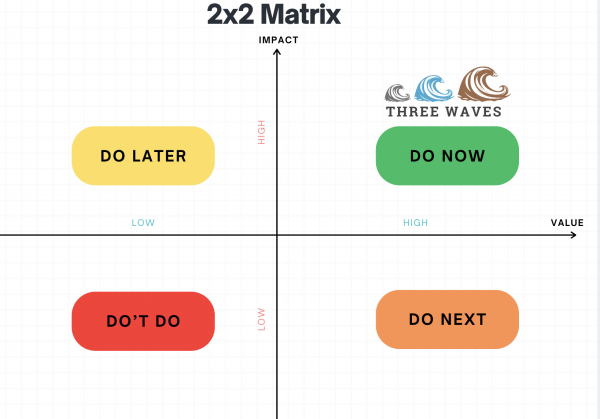
2x2 matrix diagram
- 10-step approach: It begins by building a strong foundation of AI knowledge and setting clear, achievable goals. Aligning AI initiatives with the broader business strategy is crucial, and prioritizing high-impact areas ensures maximum return on investment. Data quality is paramount, as it directly influences the accuracy and reliability of AI-driven insights. The approach emphasizes scalability, starting small, and embracing automation to streamline operations. Fostering collaboration and continuous evaluation is essential for optimizing AI solutions and adapting to evolving needs. By following these steps, the company can harness the power of AI to drive innovation, improve efficiency, and achieve sustainable growth.
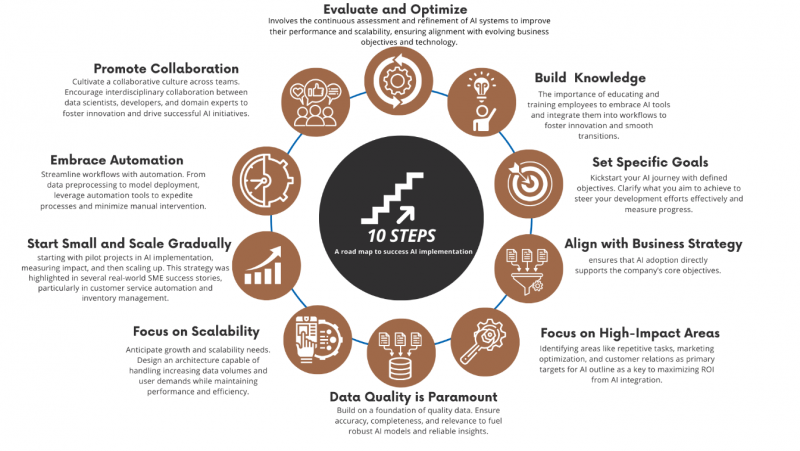
10-step approach
- Unimaginable possible 3-wave approach: Similar to a "step-by-step" strategy, It emphasizes starting small and gradually scaling up AI projects. Each wave builds upon the successes of the previous one, minimizing risks and ensuring a smooth transition before scaling up AI across the organization and core business.
Key findings of the study
The research reveals that the company is well-positioned for AI adoption, with a strong digital foundation, positive organizational culture, and strategic alignment with AI goals. However, challenges persist in system integration, infrastructure scalability, and employee skill gaps. Effective change management and targeted upskilling are essential to address concerns about role changes and ensure smooth AI adoption. Additionally, implementing a formal AI ethics policy and continuous KPI monitoring will support responsible AI use and sustained value. Closing these gaps is key to boosting operational efficiency, fostering innovation, and achieving leadership in the renewable energy consultancy sector.
Final thoughts: AI as a necessity for future competitiveness
In conclusion, integrating AI and database management technologies is no longer an option for companies in the renewable energy sector—it’s a necessity! AI supports complex project demands, enables predictive insights, and drives sustainable growth. Furthermore, AI enhances decision-making and efficiency, which are vital as the industry faces operational complexities and stringent sustainability regulations which need more innovative and data-driven approaches.
The key to success lies in a holistic approach—meaning that it addresses both humans as drivers of the innovative service offering and a technical readiness, as an enabler. It continuously evaluates the impact of the AI initiative, and it aligns AI strategies with broader business goals.
Link to the thesis:
https://www.theseus.fi/handle/10024/868532
For further reading:
Why AI and energy are the new power couple. By Rozite, V., Miller, J., & Oh, S. (2023). Commentary, International Energy Agency (IEA), Paris. https://www.iea.org/commentaries/why-ai-and-energy-are-the-new-power-couple
Artificial intelligence in the energy sector: Benefits and use cases. By Maidaniuk, O. (2024). https://intellias.com/ai-in-energy-sector-benefits/
Using digital and AI to meet the energy sector’s net-zero challenge By Medina, E., Jackson, G., & Yusuf, K. (2023). https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/quantumblack/our-insights/using-digital-and-ai-to-meet-the-energy-sectors-net-zero-challenge
About the Authors

Ali Amirnia is the main author and he is an experienced leader in technology, innovation, and digital transformation, with a career spanning in the ICT sector. His roles have ranged from Technical Design Engineer to Solution Architect, Project Manager, Sales, and Key Account Manager at companies like Ericsson. Ali is passionate about driving business strategy development, continuous improvement, and leading challenging projects. He holds a Master of Business Administration (MBA) in Digital Business and Management and a Bachelor of Science in Computer Engineering.

Rosmeriany is the second author. She is the second thesis supervisor and Head of the master’s degree program in Digital Business and Management at Novia UAS
The blog post has been reviewed by Novia's editorial board and accepted for publication on 18.12.2024.
![]()
MBA Insights
The Novia MBA Insights blog features peer-reviewed posts authored by MBA graduates and their supervisors. Its aim is to disseminate pertinent insights and findings from MBA thesis research.
The subject matter encompasses business, leadership, digitalisation, design thinking, services, project development, and may also touch on societal issues. Posts are selected for their relevance to professionals in the field or the general public.
All blog entries undergo review by a faculty editor and subject matter experts.
We follow CC-BY if nothing else is stated.
Disclaimer: The author(s) are responsible for the facts, any possible omissions, and the accuracy of the content in the blog.The texts have undergone a review, however, the opinions expressed are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the views of Novia University of Applied Sciences.
Posta din kommentar
Kommentarer
Inga har kommenterat på denna sida ännu